15 KiB
MongoDB
The database is a container of collections. The collections are containers of documents.
The documents are schema-less that is they have a dynamic structure that can change between documents in the same collection.
Data Types
| Tipo | Documento | Funzione |
|---|---|---|
| Text | "Text" |
|
| Boolean | true |
|
| Number | 42 |
|
| Objectid | "_id": {"$oid": "<id>"} |
ObjectId("<id>") |
| ISODate | "<key>": {"$date": "YYYY-MM-DDThh:mm:ss.sssZ"} |
ISODate("YYYY-MM-DD") |
| Timestamp | Timestamp(11421532) |
|
| Embedded Document | {"a": {...}} |
|
| Embedded Array | {"b": [...]} |
It's mandatory for each document ot have an unique field _id.
MongoDB automatically creates an ObjectId() if it's not provided.
Databases & Collections Usage
To create a database is sufficient to switch towards a non existing one with use <database> (implicit creation).
The database is not actually created until a document is inserted.
show dbs # list all databases
use <database> # use a particular database
show collections # list all collection for the current database
dbs.dropDatabase() # delete current database
db.createCollection(name, {options}) # explicit collection creation
db.<collection>.insertOne({document}) # implicit collection creation
Operators
/* --- Update operators --- */
{ "$inc": { "<key>": <increment>, ... } } // Increment value
{ "$set": { "<key>": "<value>", ... } } // Set value
{ "$push": { "<key>": "<value>", ... } } // add a value to an array field
/* --- Query Operators --- */
{ "<key>": { "$in": [ "<value_1>", "<value_2>", ...] } } // Membership
{ "<key>": { "$nin": [ "<value_1>", "<value_2>", ...] } } // Membership
{ "<key>": { "$exists": true } } // Field Exists
/* --- Comparison Operators (DEFAULT: $eq) --- */
{ "<key>": { "$gt": "<value>" }} // >
{ "<key>": { "$gte": "<value>" }} // >=
{ "<key>": { "$lt": "<value>" }} // <
{ "<key>": { "$lte": "<value>" }} // <=
{ "<key>": { "$eq": "<value>" }} // ==
{ "<key>": { "$ne": "<value>" }} // !=
/* --- Logic Operators (DEFAULT $and) --- */
{ "$and": [ { <statement> }, ...] }
{ "$or": [ { <statement> }, ...] }
{ "$nor": [ { <statement> }, ...] }
{ "$not": { <statement> } }
Expressive Query Operator
$<key> is used to access the value of the field dynamically
{ "$expr": { <expression> } } // aggregation expression, variables, conditional expressions
{ "$expr": { "$comparison_operator": [ "$<key>", "$<key>" ] } } // compare field values
CRUD Operations
Create
It's possible to insert a single document with the command insertOne() or multiple documents with insertMany().
Insertion results:
- error -> rollback
- success -> entire documents gets saved
# explicit collection creation, all options are optional
db.createCollection( <name>,
{
capped: <boolean>,
autoIndexId: <boolean>,
size: <number>,
max: <number>,
storageEngine: <document>,
validator: <document>,
validationLevel: <string>,
validationAction: <string>,
indexOptionDefaults: <document>,
viewOn: <string>,
pipeline: <pipeline>,
collation: <document>,
writeConcern: <document>
}
)
db.createCollection("name", { capped: true, size: max_bytes, max: max_docs_num } ) # creation of a capped collection
# SIZE: int - will be rounded to a multiple of 256
# implicit creation at doc insertion
db.<collection>.insertOne({ document }, options) # insert a document in a collection
db.<collection>.insertMany([ { document }, { document }, ... ], options) # insert multiple docs
db.<collection>.insertMany([ { document }, { document } ] , { "ordered": false }) # allow the unordered insertion, only documents that cause errors wont be inserted
NOTE: If insertMany() fails the already inserted documents are not rolled back but all the successive ones (even the correct ones) will not be inserted.
Read
db.<collection>.findOne() # find only one document
db.<collection>.find(filter) # show selected documents
db.<collection>.find(filter, {"<key>": 1}) # show selected values form documents (1 or true => show, 0 or false => don't show, cant mix 0 and 1)
db.<collection>.find(filter, {_id: 0, "<key>": 1}) # only _id can be set to 0 with other keys at 1
db.<collection>.find().pretty() # show documents formatted
db.<collection>.find().limit(n) # show n documents
db.<collection>.find().limit(n).skip(k) # show n documents skipping k docs
db.<collection>.find().count() # number of found docs
db.<collection>.find().sort({key1: 1, ... , key_n: -1}) # show documents sorted by specified keys in ascending (1) or descending (-1) order
# GeoJSON - https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/reference/operator/query/near/index.html
db.<collection>.find(
{
<location field>: {
$near: {
$geometry: { type: "Point", coordinates: [ <longitude> , <latitude> ] },
$maxDistance: <distance in meters>,
$minDistance: <distance in meters>
}
}
}
)
db.<collection>.find().hint( { "<key>": 1 } ) # specify the index
db.<collection>.find().hint( "index-name" ) # specify the index using the index name
db.<collection>.find().hint( { $natural : 1 } ) # force the query to perform a forwards collection scan
db.<collection>.find().hint( { $natural : -1 } ) # force the query to perform a reverse collection scan
Update
db.<collection>.updateOne(filter, $set: {"<key>": value}) # add or modify values
db.<collection>.updateOne(filter, $set: {"<key>": value}, {upsert: true}) # add or modify values, if attribute doesn't exists create it
db.<collection>.updateMany(filter, update)
db.<collection>.replaceOne(filter, { document }, options)
Delete
db.<collection>.deleteOne(filter, options)
db.<collection>.deleteMany(filter, options)
db.<collection>.drop() # delete whole collection
db.dropDatabase() # delete entire database
Mongoimport
Utility to import all docs into a specified collection.
If the collection already exists --drop deletes it before reuploading it.
WARNING: CSV separators must be commas (,)
mongoimport <options> <connection-string> <file>
--uri=<connectionString>
--host=<hostname><:port>, -h=<hostname><:port>
--username=<username>, -u=<username>
--password=<password>, -p=<password>
--collection=<collection>, -c=<collection> # Specifies the collection to import.
--ssl # Enables connection to a mongod or mongos that has TLS/SSL support enabled.
--type <json|csv|tsv> # Specifies the file type to import. DEFAULT: json
--drop # drops the collection before importing the data from the input.
--headerline # if file is CSV and first line is header
--jsonarray # Accepts the import of data expressed with multiple MongoDB documents within a single json array. MAX 16 MB
Mongoexport
Utility to export documents into a specified file.
mongoexport --collection=<collection> <options> <connection-string>
--uri=<connectionString>
--host=<hostname><:port>, -h=<hostname><:port>
--username=<username>, -u=<username>
--password=<password>, -p=<password>
--db=<database>, -d=<database>
--collection=<collection>, -c=<collection>
--type=<json|csv>
--out=<file>, -o=<file> #Specifies a file to write the export to. DEFAULT: stdout
--jsonArray # Write the entire contents of the export as a single json array.
--pretty # Outputs documents in a pretty-printed format JSON.
--skip=<number>
--limit=<number> # Specifies a maximum number of documents to include in the export
--sort=<JSON> # Specifies an ordering for exported results
Mongodump & Mongorestore
mongodump exports the content of a running server into .bson files.
mongorestore Restore backups generated with mongodump to a running server.
Relations
Nested / Embedded Documents:
- Group data logically
- Optimal for data belonging together that do not overlap
- Should avoid nesting too deep or making too long arrays (max doc size 16 mb)
{
"_id": Objectid()
"<key>": "value"
"<key>": "value"
"innerDocument": {
"<key>": "value"
"<key>": "value"
}
}
References:
- Divide data between collections
- Optimal for related but shared data used in relations or stand-alone
- Allows to overtake nesting and size limits
NoSQL databases do not have relations and references. It's the app that has to handle them.
{
"<key>": "value"
"references": ["id1", "id2"]
}
// referenced
{
"_id": "id1"
"<key>": "value"
}
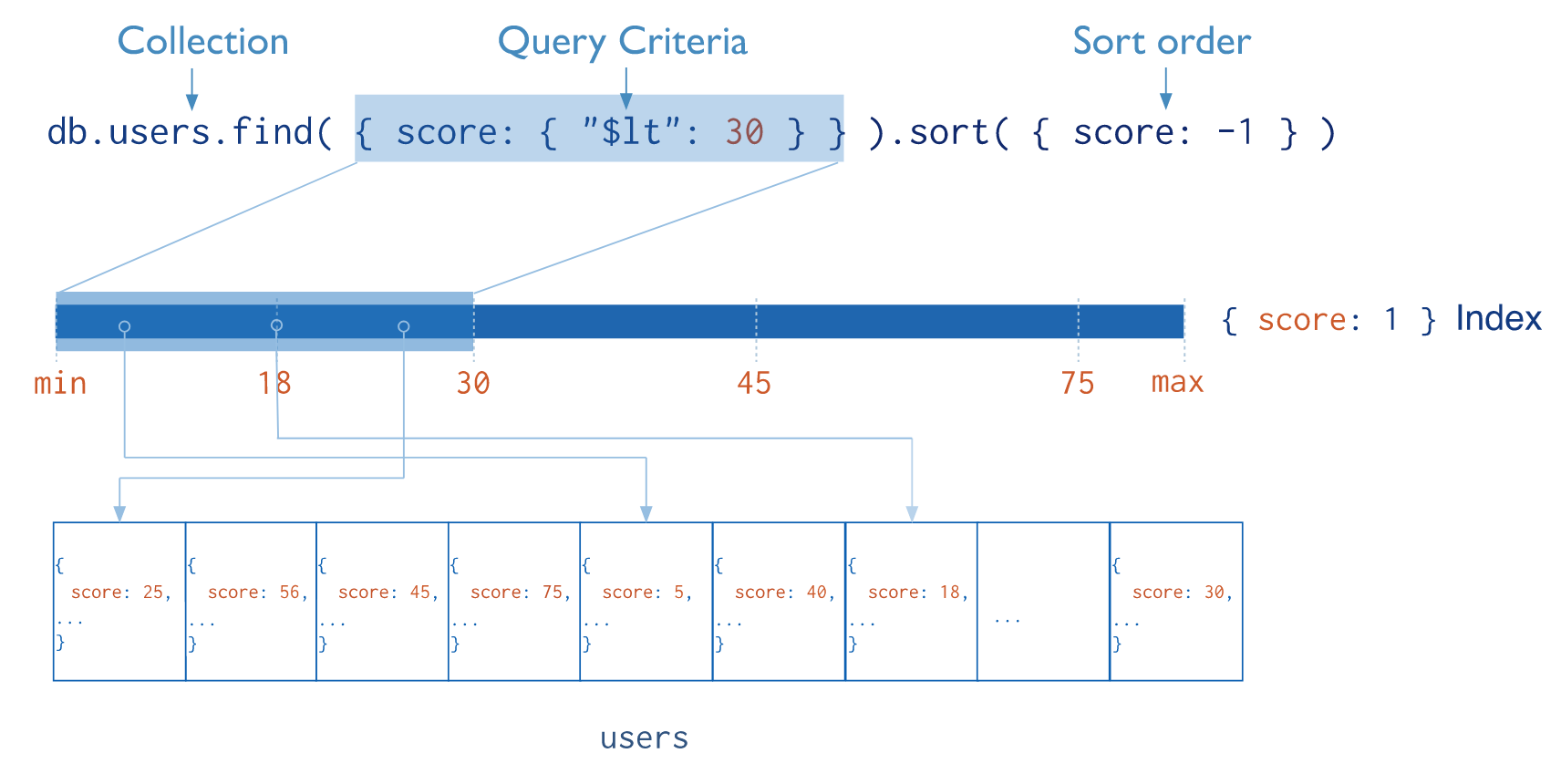
Indexes
Indexes support the efficient execution of queries in MongoDB.
Without indexes, MongoDB must perform a collection scan (COLLSCAN): scan every document in a collection, to select those documents that match the query statement.
If an appropriate index exists for a query, MongoDB can use the index to limit the number of documents it must inspect (IXSCAN).
Indexes are special data structures that store a small portion of the collection's data set in an easy to traverse form. The index stores the value of a specific field or set of fields, ordered by the value of the field. The ordering of the index entries supports efficient equality matches and range-based query operations. In addition, MongoDB can return sorted results by using the ordering in the index.
Indexes slow down writing operations since the index must be updated at every writing.
Index Types
- Normal: Fields sorted by name
- Compound: Multiple Fields sorted by name
- Multikey: values of sorted arrays
- Text: Ordered text fragments
- Geospatial: ordered geodata
Sparse indexes only contain entries for documents that have the indexed field, even if the index field contains a null value. The index skips over any document that is missing the indexed field.
Diagnosis and query planning
db.<collection>.find({...}).explain() # explain won't accept other functions
db.explain().<collection>.find({...}) # can accept other functions
db.explain("executionStats").<collection>.find({...}) # more info
Index Creation
db.<collection>.createIndex( <key and index type specification>, <options> )
db.<collection>.createIndex( { "<key>": <type>, "<key>": <type>, ... } ) # normal, compound or multikey (field is array) index
db.<collection>.createIndex( { "<key>": "text" } ) # text index
db.<collection>.createIndex( { "<key>": 2dsphere } ) # geospatial 2dsphere index
# sparse index
db.<collection>.createIndex(
{ "<key>": <type>, "<key>": <type>, ... },
{ sparse: true } # sparse option
)
# custom name
db.<collection>.createIndex(
{ <key and index type specification>, },
{ name: "index-name" } # name option
)
Index Management
# view all db indexes
db.getCollectionNames().forEach(function(collection) {
indexes = db[collection].getIndexes();
print("Indexes for " + collection + ":");
printjson(indexes);
});
db.<collection>.getIndexes() # view collection's index
db.<collection>.dropIndexes() # drop all indexes
db.<collection>.dropIndex( { "index-name": 1 } ) # drop a specific index
Database Profiling
Profiling Levels:
0: no profiling1: data on operations slower thanslowms2: data on all operations
Logs are saved in the system.profile capped collection.
db.setProfilingLevel(n) # set profiler level
db.setProfilingLevel(1, { slowms: <ms> })
db.getProfilingStatus() # check profiler status
db.system.profile.find().limit(n).sort( {} ).pretty() # see logs
db.system.profile.find().limit(n).sort( { ts : -1 } ).pretty() # sort by decreasing timestamp
Roles and permissions
Authentication: identifies valid users Authorization: identifies what a user can do
- userAdminAnyDatabase: can admin every db in the instance (role must be created on admin db)
- userAdmin: can admin the specific db in which is created
- readWrite: can read and write in the specific db in which is created
- read: can read the specific db in which is created
# create users in the current MongoDB instance
db.createUser(
{
user: "dbAdmin",
pwd: "password",
roles:[
{
role: "userAdminAnyDatabase",
db:"admin"
}
]
},
{
user: "username",
pwd: "password",
roles:[
{
role: "role",
db: "database"
}
]
}
)
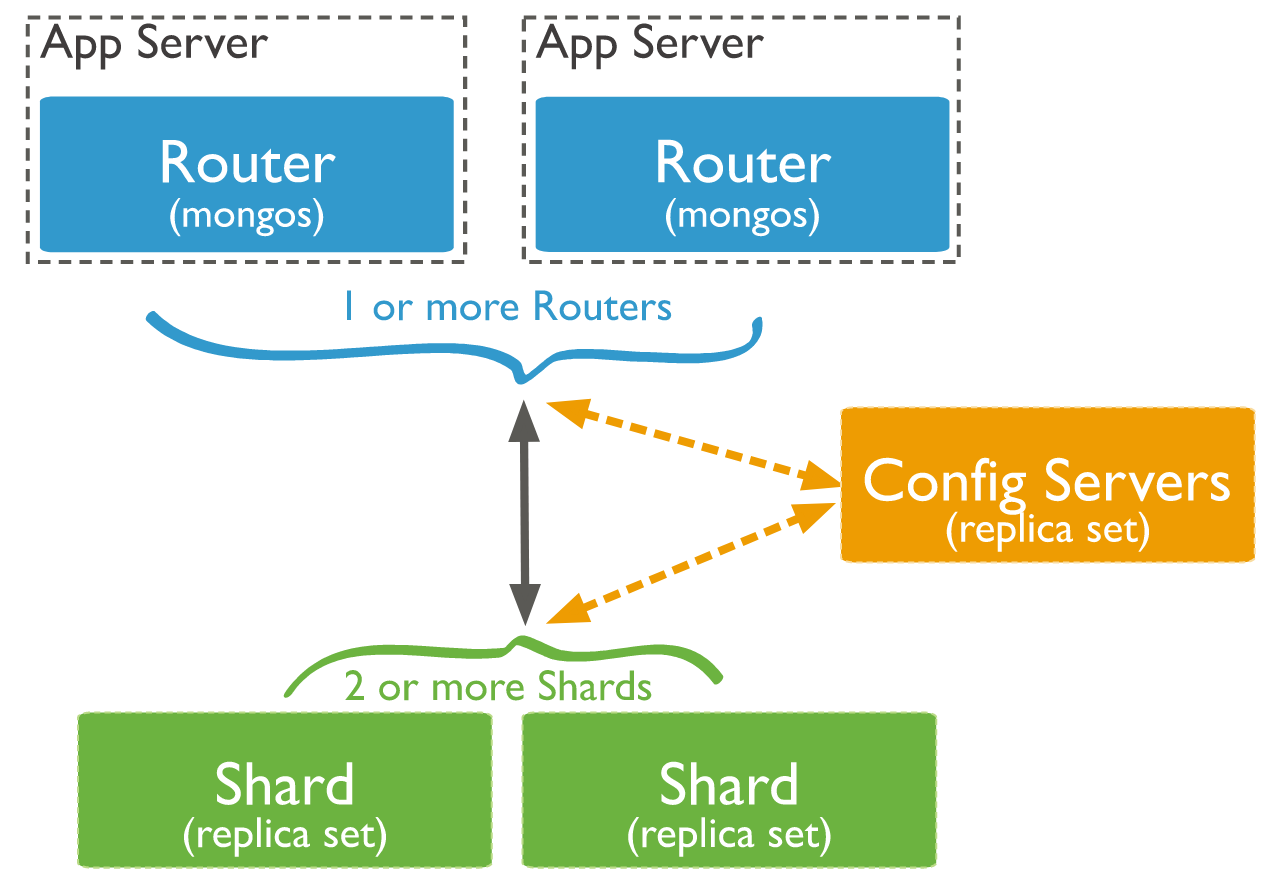
Sharding
Sharding is a MongoDB concept through which big datasets are subdivided in smaller sets and distributed towards multiple instances of MongoDB.
It's a technique used to improve the performances of large queries towards large quantities of data that require al lot of resources from the server.
A collection containing several documents is splitted in more smaller collections (shards) Shards are implemented via cluster that are none other a group of MongoDB instances.
Shard components are:
- Shards (min 2), instances of MongoDB that contain a subset of the data
- A config server, instance of MongoDB which contains metadata on the cluster, that is the set of instances that have the shard data.
- A router (or
mongos), instance of MongoDB used to redirect the user instructions from the client to the correct server.
Replica set
A replica set in MongoDB is a group of mongod processes that maintain the same dataset. Replica sets provide redundancy and high availability, and are the basis for all production deployments.
Aggregations
Sequence of operations applied to a collection as a pipeline to get a result: db.collection.aggregate(pipeline, options).
$lookup: Right Join$match: Where$sort: Order By$project: Select *- ...
Example:
db.collection.aggregate([
{
$lookup: {
from: <collection to join>,
localField: <field from the input documents>,
foreignField: <field from the documents of the "from" collection>,
as: <output array field>
}
},
{ $match: { <query> } },
{ $sort: { ... } },
{ $project: { ... } },
{ ... }
])